Case Studies
EM Bokashi Pilot Tests Explore New Sustainable Solutions
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland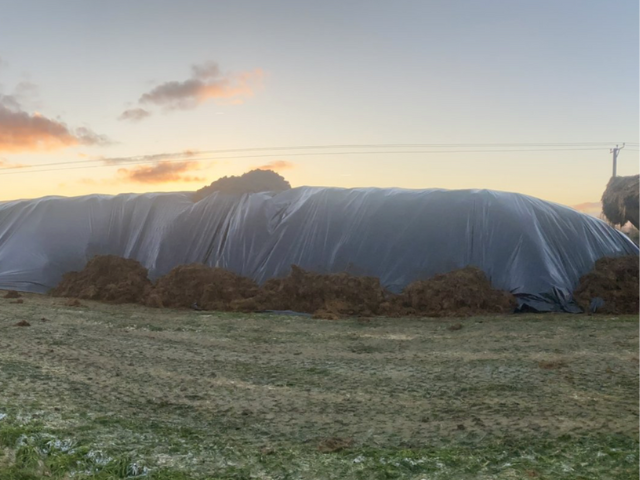
Overview
EM Agriton in UK has a long experience in providing EM Bokashi and researching on its applications. They recently support trials of EM Bokashi for treating farmyard manure while collecting data to refine and promote a sustainable manure management technique and giving technical advice.
Problems
Cattle farmers face challenges with manure management, including strong odors affecting workers and neighbors, pathogens that can contaminate both livestock and humans, and greenhouse gas emissions such as methane and ammonia, which impact to climate change. In addition, managing nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus to prevent runoff and water pollution is critical.
All of these problems are essential to mitigate, but are costly.
All of these problems are essential to mitigate, but are costly.
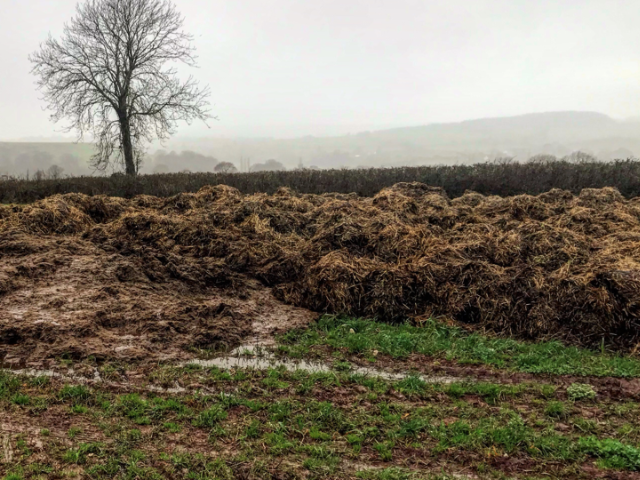


EM Application
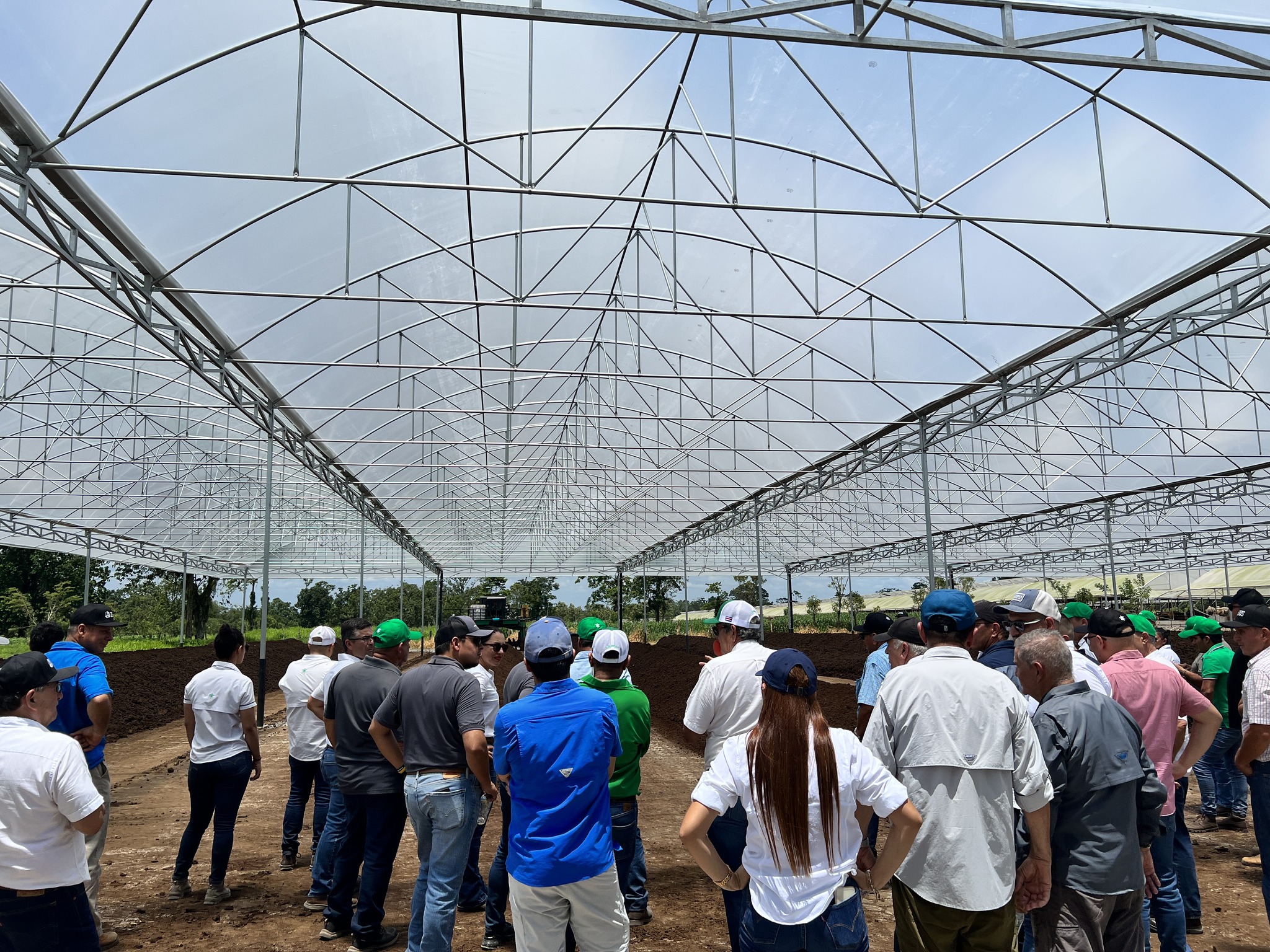
In seeking a solution, two farmers in Scotland have teamed up with a soil expert to explore the practical benefits of using EM Bokashi and EM Technology for treating manure, including breaking down animal bedding and dung over a period of 3 years.
The steps they took to manage manure with EM Bokashi were as follows:
1. Spread the organic matter to create a layer.
2. Apply Activated EM・1 (AEM) and clay minerals to the layer.
3. Repeat the previous steps to create additional layers.
4. Cover the manure with a plastic sheet to create anaerobic conditions, and leave it for 6-8 weeks.
The steps they took to manage manure with EM Bokashi were as follows:
1. Spread the organic matter to create a layer.
2. Apply Activated EM・1 (AEM) and clay minerals to the layer.
3. Repeat the previous steps to create additional layers.
4. Cover the manure with a plastic sheet to create anaerobic conditions, and leave it for 6-8 weeks.
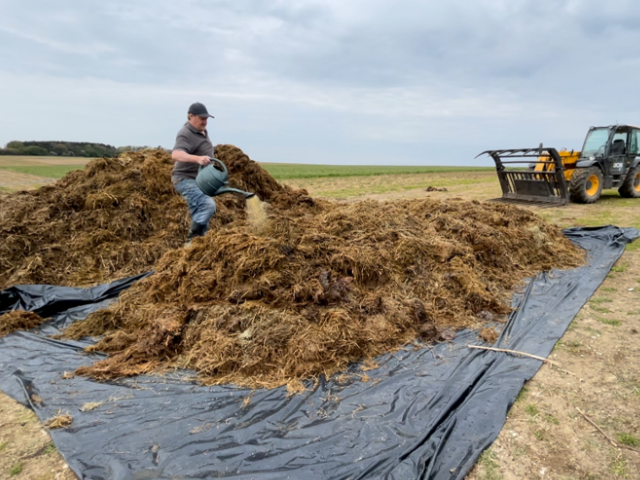
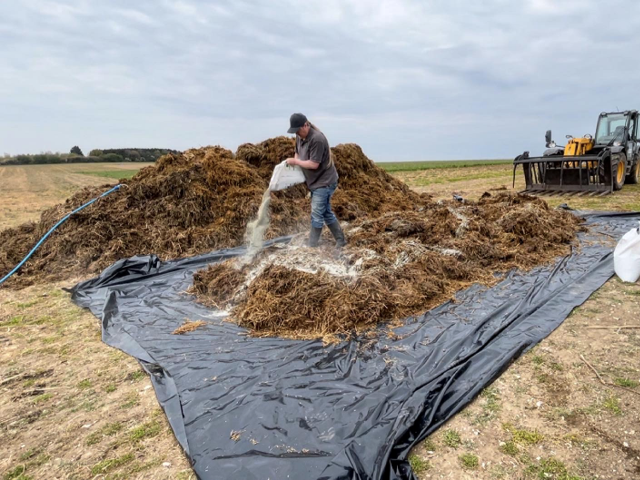
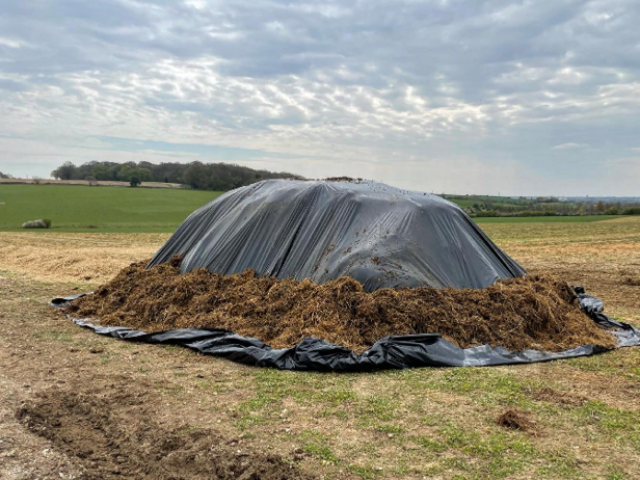



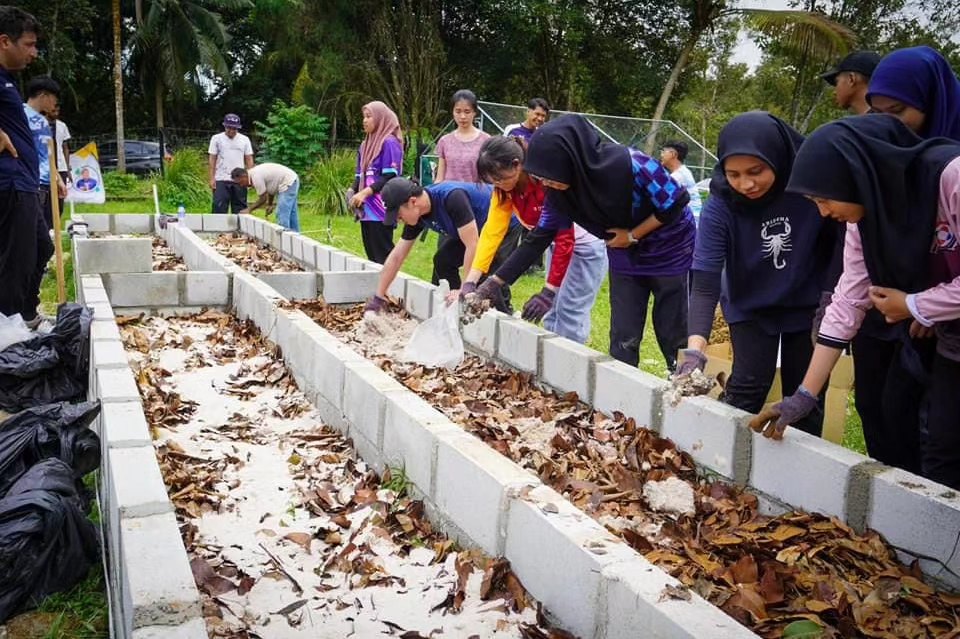
(Photo: 1,2,3) EM Bokashi treatment: AEM and clay minerals are applied in layers and then covered with a plastic sheet.,
Effects and Results
According to farmers’ feedback:
- EM Bokashi treatment retains nutrients (C, N, P) in manure and reduces methane and ammonia emissions.
- EM Bokashi manure smells sweet and solves odor problems due to lower ammonia emissions. - EM Bokashi manure treatment method is easier to handle than conventional aerobic composting and is more cost effective.
- Applying EM Bokashi manure in farming improved soil health, leading to healthier crops and better yields.
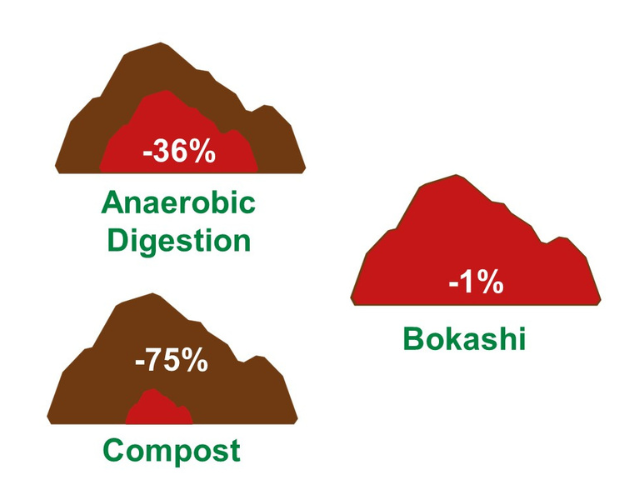
- Researches indicates that fermentation (EM Bokashi treatment) and anaerobic digestion conserved 99% and 64% of C; and 93% and 100% of N, respectively. While conventional compost conservation of nutrients is limited to 25% of C and 38% of N (see Reference).
- Positive results in nutrient management and methane reduction could open new opportunities in carbon footprint management.
- EM Bokashi treatment retains nutrients (C, N, P) in manure and reduces methane and ammonia emissions.
- EM Bokashi manure smells sweet and solves odor problems due to lower ammonia emissions. - EM Bokashi manure treatment method is easier to handle than conventional aerobic composting and is more cost effective.
- Applying EM Bokashi manure in farming improved soil health, leading to healthier crops and better yields.
- Researches indicates that fermentation (EM Bokashi treatment) and anaerobic digestion conserved 99% and 64% of C; and 93% and 100% of N, respectively. While conventional compost conservation of nutrients is limited to 25% of C and 38% of N (see Reference).
- Positive results in nutrient management and methane reduction could open new opportunities in carbon footprint management.

Reference
Vania Scarlet Chavez-Rico, Paul L.E. Bodelier, Miriam van Eekert, Valentina Sechi, Adrie Veeken, Cees Buisman, 2022
 Producing organic amendments: Physicochemical changes in biowaste used in anaerobic digestion, composting, and fermentation
Producing organic amendments: Physicochemical changes in biowaste used in anaerobic digestion, composting, and fermentation
Waste Management, Volume 149, 15 July 2022, Pages 177-185
*EM AGRITON BV in the Netherlands collaborated in this research.
Vania Scarlet Chavez-Rico, Paul L.E. Bodelier, Miriam van Eekert, Valentina Sechi, Adrie Veeken, Cees Buisman, 2022
Waste Management, Volume 149, 15 July 2022, Pages 177-185
*EM AGRITON BV in the Netherlands collaborated in this research.
For further information, please contact our partner at:
EM Agriton Limited.
 Ebear Farm, Westleigh, Tiverton, EX16 7HN. Devon. UK.
Ebear Farm, Westleigh, Tiverton, EX16 7HN. Devon. UK.
 Phone: +44-(0)-1823-67-33-44
Phone: +44-(0)-1823-67-33-44
 E-mail: info@agriton.co.uk
E-mail: info@agriton.co.uk
EM Agriton Limited.
(June 2024)

















































































